
Using the NAPA NP-Cath™ for Measuring Dynamic PEEP during NHF Therapy
Measuring NHF Pressure is now possible to assure that NHF is applied at safe and optimal therapeutic levels.*
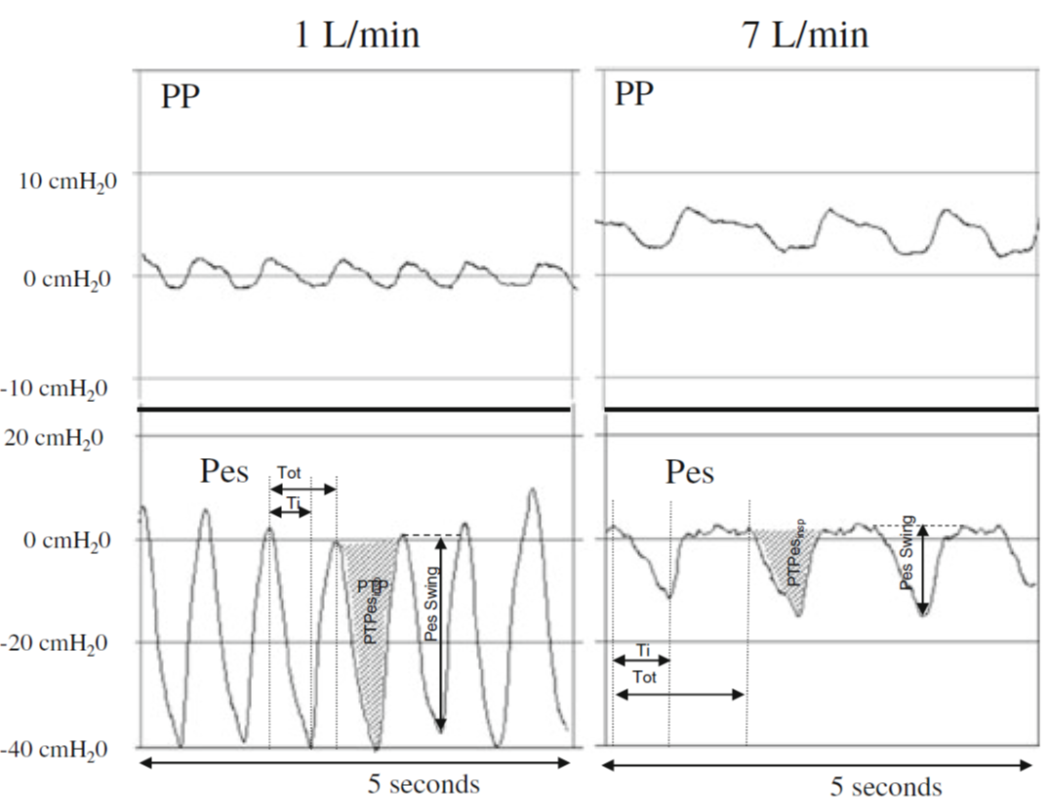
NHF settings are typically set at 2–4 lpm, which can often cause patients to experience air hunger since flow is not meeting or exceeding peak inspiratory flow.
Meeting or exceeding inspiratory flows has been shown to decrease WOB and create a dynamic PEEP effect which increases FRC and maintains lung function.
When transitioning from a (B)CPAP of 5 or 6 cm/H2O and going to NHF of 4 LPM, there is a significant drop in supportive pressure and as a result, it may take a while for the infant to recover, or this may cause a failure in NHF therapy.
By utilizing the NP-Cath™ for measuring the dynamic PEEP, the flow rate can be safely adjusted to achieve the pressure-targeted level, typically achieved at flows of 6–8 lpm on a neonate. NHF at 6-8 lpm has been shown to deliver approx. 4–6 cm/H20, much like that of standard CPAP.
By placing the NP-Cath™ approx. 1-2 cm into the nare, accurate pressures can be acquired in the nasal pharyngeal space which are proportional to the delivered lung pressures.
- The only way to assure you are meeting or exceeding inspiratory demand is by measuring the mean airway pressure to verify that the flow is creating positive pressure.
- Meeting inspiratory demand during NHF Therapy can decrease WOB and optimize outcomes –Fratzke 2019
- Creating a dynamic PEEP with NHF has clinically significant effects on infant –Liew 2019
*When used in conjunction with the NAPA Monitor
Clinically Significant Dynamic PEEP Comparable to Conventional CPAP
- Front Line Therapy for Respiratory Distress
- Meet Patient Inspiratory Demands
- Decrease WOB
- Result-Based vs Weight-Based Flow Guidelines
- Smooth Transition to NHF from CPAP or Extubation
THERE IS SAFETY IN
(KNOWING THE) NUMBERS
Measuring NHF Pressures with the New NP-CATH
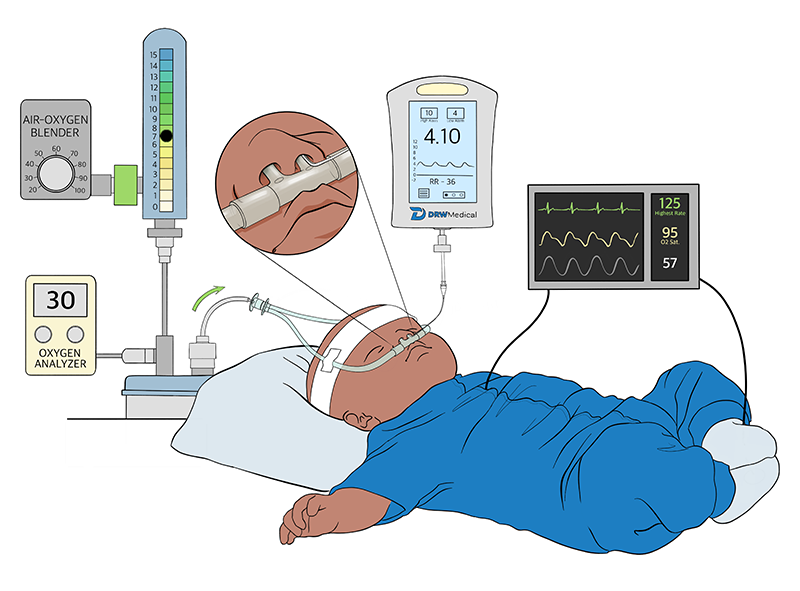
Simply insert the NP-Cath™ into nares approximately 2 cm to obtain a reading. Flows of 6 liters or more are needed to generate a dynamic PEEP.
Documentation
Pharyngeal pressure with high-flow nasal cannulae in premature infants
Journal of Perinatology
High-flow nasal cannula: recommendations for daily practice in pediatrics
PDF brochure for the NAPA LP-15 Neonatal Airway Pressure Monitor


